



Plant Scope
Disease can negatively impact plant health before any visible signs like leaf discoloration. While these stresses are invisible to our naked eye, drone cameras using special filters could detect these subtle changes in real-time. Evidence has shown that drone remote imagery can help to identify disease related stress in plants. However, could the spectral signatures of infected plants be unique enough to differentiate the causal disease remotely and how could we use this to reduce the burden on inspectors in the field or better target our inspections? Our Multi-spectral and hyper-spectral imagery are often used to measure the responses of plants in the visible and near infrared parts of the electromagnetic spectrum to remotely detect plant stress using drone technology.
How the System Works
We train and test our systems end-to-end on our large Pests and diseases Data set, which contains challenging images with diseases and pests, including several inter and extra class variations, such as infection status and location of the plant where it has been taken from. Experimental results show that our proposed system can effectively recognize seven different types of diseases and pests, with the ability to deal with complex scenarios from a plant’s surrounding area. Diseases reduce yields when we need them to be high, as the global population grows and we need to feed more people than ever. Reducing yield loss to diseases like Cercospora leaf spot in Maize, Rice Tungro disease, cassava mosaic disease and many others will allow us to grow more food, more efficiently and on less land, benefiting the agricultural industry, the public and the environment.
A farmer can use a drone to detect any anomalies, upload a photo of infected crops and send it offline to the farmer’s mobile app. The mobile app does the processing, it broadcasts that disease to the nearby farmers within that community with all descriptions about that disease, the contact and location of the specialized agronomist to work on that crop and give advice in real-time. Besides giving a diagnosis and steps to mitigate the disease, the app also provides information on preventing the disease in the next cropping season.
Plants We Support
With the power of machine learning, we integrate the latest technologies into agriculture and make them accessible to everyone at all times. This is our contribution to securing global food production. Specializing in agricultural crops that feed the world, Plant Scope empowers farmers to make a living by providing comprehensive support on all issues that are important to farmers.

Banana
After wheat, rice, and corn, bananas are the fourth most important crop in the world. 90 percent of the world’s banana production is grown on small farms in tropical developing countries. Bananas are the most important staple food for around 400 million people.

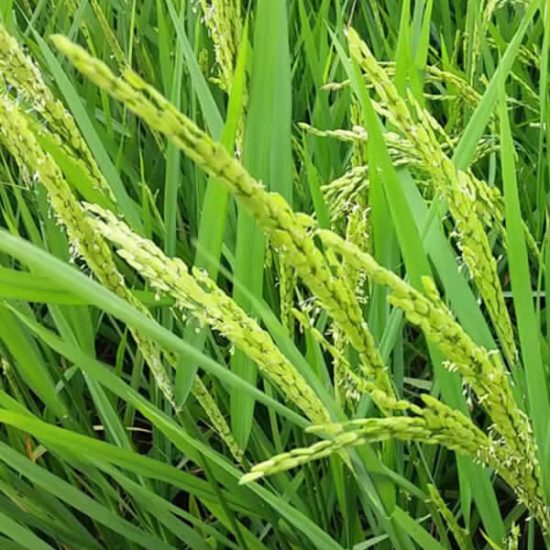
Rice
Rice, also known as paddy, is the most important food crop in the world. No field crop in the world is cultivated more than rice. No other plant feeds more people than rice. There are 144 million rice farms with a total size of 158 million hectares.

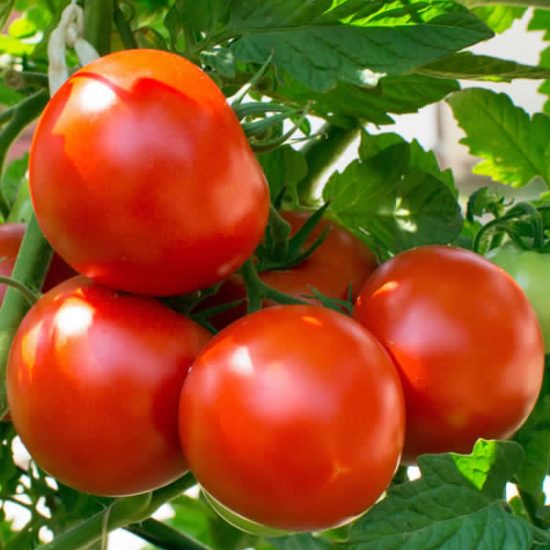
Tomato
The tomato is a major vegetable crop that is grown in practically every country in the world. Farmers worldwide produce more than 160 million tons of tomatoes every year. About 5 million hectares of tomatoes are planted all over the Earth.

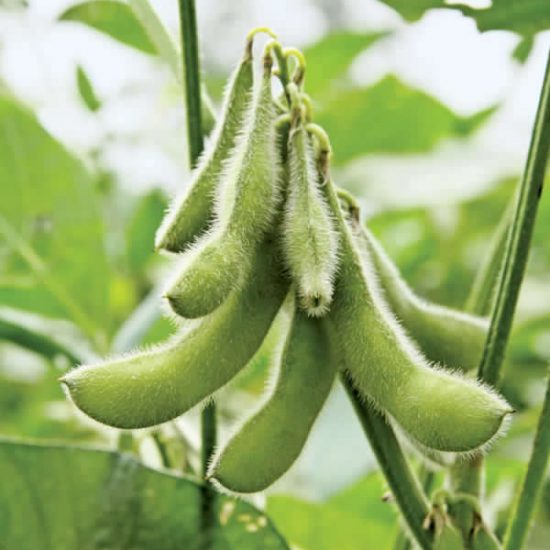
Soyabean
Soybeans are among the most valuable crops in the world. On average, more than 230 million tons of soy are produced annually. Of these, 92% are produced in the USA, Brazil, Argentina, China, and India.

Bean
Beans are grown in more than 120 countries. Worldwide, more than 23 million tonnes are produced every year.

Maize
Maize, also known as corn, can be processed into a variety of food and industrial products. It is an important food plant in Africa, Latin America, and Asia. The United States, China and Brazil are the world’s three largest maize producers – producing annually around 563 of the 717 million tonnes.

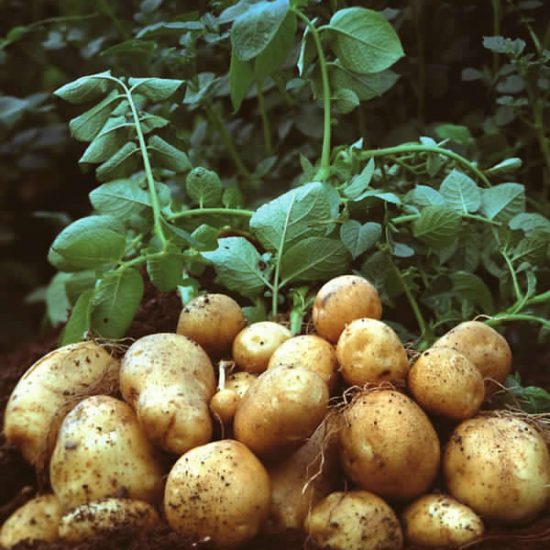
Cassava
Cassava is the third-largest source of food carbohydrates in the tropics, after rice and maize. Cassava is a major staple food in the developing world, providing a basic diet for over half a billion people. It is one of the most drought-tolerant crops, capable of growing on marginal soils.

Apple
Apple trees are large if grown from seed. Generally, apple cultivars are propagated by grafting onto rootstocks, which control the size of the resulting tree. There are more than 7,500 known cultivars of apples, resulting in a range of desired characteristics. Different cultivars are bred for various tastes and use, including cooking, eating raw and cider production.
Discover the benefits of using the Plant Scope App
Plant Scope uses algorithms to integrate and analyze the captured images and data to provide a detailed report on the health accurately and faster to detect diseases and pests in plants. This helps farmers in early treatment technique while substantially reducing economic losses. The ability to control disease early enough is a top priority for farmers and an ongoing challenge such as herbicide resistance becomes more common.
How It Works

No Lab Needed
Our system uses images of plant diseases and pests taken in-place, thus we avoid the process of collecting samples and analyzing them in the laboratory.

Our Approach
Our approach uses input images captured by different camera devices with various resolutions such as drone, cell phone and other digital cameras.
It's Efficient
It can efficiently deal with different illumination conditions, the size of objects, and background variations, etc., contained in the surrounding area of the plant.












